The Australian Professional Standards for Teachers (the Standards) have a common language, also known as the “lexical fingerprint”. The lexical fingerprint refers to the different patterns of words that appear across the career stages.
We can look at the quantitative patterns – the frequency of words– and the qualitative patterns – the word associations. These patterns are not accidental. The deliberate and careful word choices helps to construct professional identities
across the four-stage career continuum in the Standards.
Becoming more familiar with the lexical fingerprint will help you to assess your own practice and identify areas for growth and development. Teachers and leaders sharing a common language means they can more easily provide effective feedback to colleagues.
The following video features Associate Professor Joy Hardy introducing the lexical patterns of Standards. This video will give you an initial introduction to the content of this module and revisiting it after reading may help consolidate your learning.
https://vimeo.com/721025695/e8c44dee75
Video notes
The Standards policy document has a brief career stage overview, and we can see some early patterns coming through there. Certain terms may be associated more with particular career stages, for example:
- ‘qualification’ is used exclusively in the Graduate career stage
- ‘specialist’ is used exclusively in the Highly Accomplished career stage
- ‘inspire’ and ‘exemplary’ are used exclusively in the Lead career stage.
The terms ‘effectively’ and ‘understand/ing’ (by teachers) are used across all career stages, although their distribution is uneven:
- ‘effective/ly’ appears increasingly as you move up through the stages
- ‘understanding’ is used predominately in relation to the Graduate career stage.
These patterns are specific to the career stage overview in the Standards, with more lexical patterns to be found in the descriptors of the Standards themselves.
“Quantitative lexical patterns” refers to how often we see particular words or terms coming up in the Standards.
Fairly equal frequency across the career stages: parents, assessment, knowledge, learning, student(s)
Uneven frequency across the career stages: demonstrate
Exclusively for particular career stages: exemplary, lead
Frequencies of selected lexical items across career stages
Lexical item (Word) | Frequency |
|---|
Graduate | Proficient | Highly Accomplished | Lead |
|---|
Parents | 3 | 3 | 3 | 5 |
Assessment | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
Knowledge | 14 | 8 | 10 | 12 |
Learning | 19 | 23 | 24 | 23 |
Student(s) | 21 | 24 | 22 | 24 |
Demonstrate | 21 | 0 | 1 | 4 |
Exemplary | 0 | 0 | 0 | 6 |
Lead | 0 | 0 | 0 | 20 |
Activity
For this task, you will investigate quantitative patterns in the Descriptors for each career stage by examining a series of word clouds . The word clouds are constructed by looking at the frequency of words. A large font size signifies high frequency,
a small font size indicates that word doesn’t appear often.
Graduate career stage
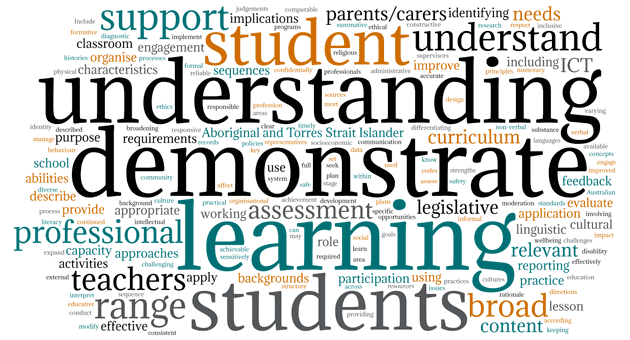
Proficient career stage

Highly accomplished career stage

Lead career stage

What distinctive lexical patterns can you see?
What are the most prominent verbs in the Highly Accomplished and Lead career stage word clouds?
You may have noticed there aren’t prominent verbs in the Proficient word cloud. Why do you think this is?
Increased frequency does not always equate with increased noteworthiness. Identify some low-frequency words that you consider to be highly notable. In saying this, assigning significance can be problematic. Why do you think this is?
Deeper delve than word frequency
When looking at lexical patterns (the frequency of words), you should also consider the collocations (word combinations). Firth once stated, “You shall know a word by the company it keeps” (Firth 1957, p. 11 ). Words keep different company
across each career stage, as shown in the table below.
Collections of the term ‘demonstrate’ across the career stages
Graduate
1.1 Demonstrate knowledge and understanding of...
1.2 Demonstrate knowledge and understanding of...
1.3 Demonstrate knowledge of....
1.4 Demonstrate broad knowledge and understanding of...
1.5 Demonstrate knowledge and understanding
of...
1.6 Demonstrate broad knowledge of...
2.1 Demonstrate knowledge and understanding of...
2.4 Demonstrate broad knowledge of understanding of and respect...
3.4 Demonstrate knowledge of...
3.5 Demonstrate a range of...
3.6 Demonstrate broad knowledge of...
4.3 Demonstrate knowledge of...
4.2 Demonstrate the capacity to...
4.5 Demonstrate an understanding of...
5.1 Demonstrate understanding of...
5.2 Demonstrate an understanding of...
5.3 Demonstrate understanding of...
5.4 Demonstrate the capacity to...
5.5 Demonstrate understanding of...
6.1 Demonstrate an understanding of...
6.4 Demonstrate an understanding of...
Proficient
None
Highly Accomplished
7.3 Demonstrate responsiveness in all...
Lead
2.1 Demonstrate exemplary teaching of...
3.1 Demonstrate exemplary practice and...
3.5 Demonstrate and lead by example...
4.1 Demonstrate and lead by example...
- At the Graduate career stage, ‘demonstrating’ refers to the teacher having a (broad) knowledge and/or understanding and/or capacity
- At the Lead career stage, ‘demonstrating’ refers to the teacher demonstrating exemplary practice/teaching and ‘demonstrating’ through leading.
Looking at the lexical patterns alone will not give you a full picture. For example, the word ‘support’ can be found in all four career stages, however, it is how the word is used that is important.
In understanding the lexical patterns of the Standards you can have more constructive conversations with colleagues. When you are reflecting on your practice, using lexical patterns (including collocations) to frame your thinking will enable you to view
your practice in a different light.
This will allow you to match your current practice with the relevant career stage within the Standards.
Reflection
What are some other ways that you might be able to use lexical patterns in your teaching practice?
Some terms are associated exclusively with particular career stage descriptions; others are used more frequently with a particular career stage description, and some terms are distributed fairly evenly across the career stage descriptions.
Examples of terminology across career stages |
|---|
Qualification | Graduate |
Specialist | Highly Accomplished |
Inspire | Lead |
Exemplary | Lead |
Effectively | Used across the career stages, although its distribution is uneven. It is used increasingly across the career stage trajectory. |
Understand/ing | Used across the career stages, although its distribution is uneven. It is used predominately in relation to the Graduate career stage. |
Let’s watch another video with Associate Professor Joy Hardy. Here, she explains how terminology is used within the Standards to construct specific identities and relationships.
https://player.vimeo.com/video/721032884?h=15ca250e1c
Video notes
Activity
Download the Descriptors across the four career stages.
Using the search function, record the number of occurrences of each term in the table below.
Terms | Graduate | Proficient | Highly Accomplished | Lead |
|---|
Lead colleagues | | | | |
Support colleagues | | | | |
Assist colleagues | | | | |
Work with colleagues | | | | |
Advice from colleagues | | | | |
Feedback from colleagues | | | | |
Looking at your results, what are the different word associations with ‘colleagues’ across the four career stages?
What role do Highly Accomplished teachers play in relation to their colleagues? How does this differ to Lead teachers?
If you found this activity interesting, you can also investigate other collocations across the career stages.
Professional conversation
Discuss your findings about lexical patterns with a colleague. What are your next steps to maximise your impact and scaffold your learning journey?
Deepen your understanding with the next module:
Alternatively, return to the: